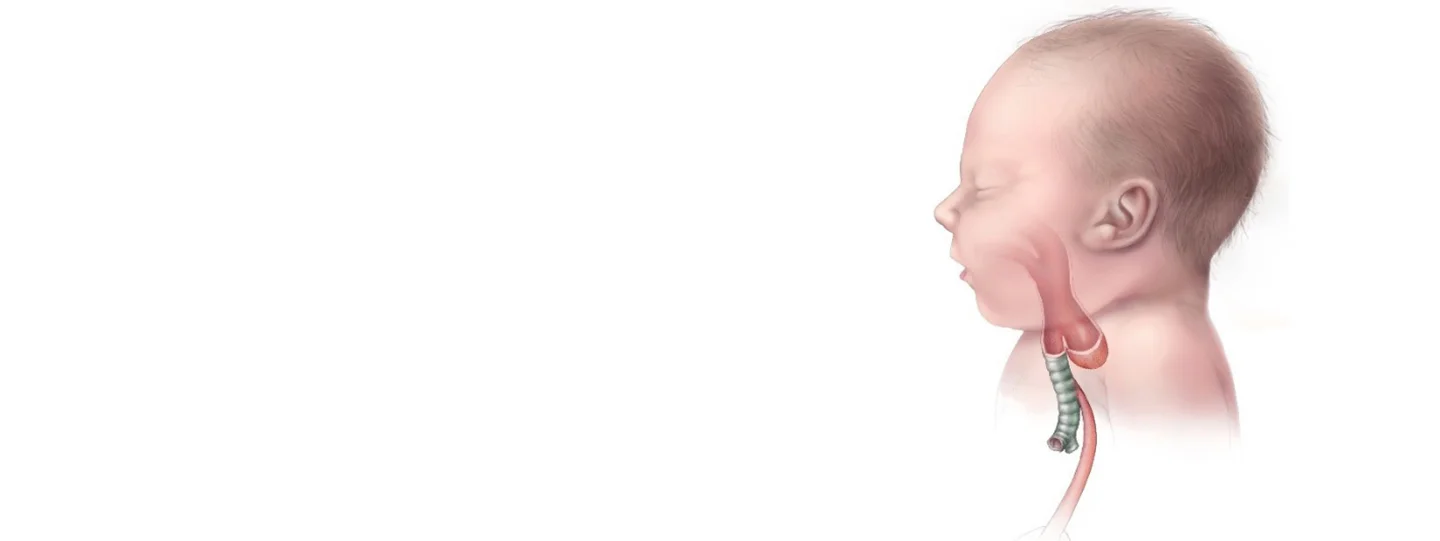

A congenital deformity that affects how your baby's esophagus grows is called esophageal atresia. The swallowing tube that joins their mouth and stomach is called the esophagus. "Atresia" refers to the absence or closure of a channel within the body. The esophagus is blocked at the bottom where it should join your baby's stomach in esophageal atresia. Your infant can't eat regularly because of this.
There are various forms of esophageal atresia, some of which can cause extra challenges for your baby. Up to 90% of babies with esophageal atresia also have a tracheoesophageal fistula, which is a birth defect in which the esophagus connects to the trachea, or windpipe, rather than the stomach, which can cause the baby to choke or inhale when they swallow
The many forms of esophageal atresia (EA), with or without tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF), are characterized by where the esophagus closes and, if it does, where it attaches to the trachea.
| Type of Esophageal Atresia | Description |
| Type A | The esophagus ends in a closed pouch and does not connect to the stomach. No tracheoesophageal fistula is present. This is a classical but less common form. |
| Type B | The lower esophagus ends blindly, while the upper part connects to the trachea through a fistula. This type is very rare. |
| Type C | The most common form. The upper esophagus ends in a closed pouch, and the lower part connects to the trachea and the stomach. |
| Type D | The rarest and most severe form. Both upper and lower segments of the esophagus connect separately to the trachea through two different fistulas. |
Congenital malformations, such as esophageal atresia, occur when something in the oesophagus develops differently during fetal development and results in an impairment that exists from birth. As the esophagus and trachea develop normally, they start off as a single tube and eventually split apart. In case, this tube fails to complete its development and separation, esophageal atresia (and frequently tracheoesophageal fistula) forms.
Another question is what hinders this process of development. Although the precise reasons are unknown, researchers believe that both genetic and environmental factors have a role. Genetic mutations are alterations to your child's DNA that impact their development. Both random and partially inherited mutations can be the possible causes. Stress and other environmental variables can increase the likelihood of mutations.
Babies may have trouble swallowing due to esophageal abnormalities. Although most forms of esophageal atresia do not cause breathing problems. When these issues appear simultaneously, it typically means that EA has TEF.
Experts recognize esophageal atresia by the “three Cs”:
Other signs and symptoms can include:
Soon after your baby is born, surgery may often correct the abnormalities. Before they are prepared for the procedure, some newborns might need to remain in the hospital for a short while longer in order to get respiratory assistance and feeding. If their esophagus is too short to heal or they were born prematurely, they could require additional time to grow. Treatment for other life-threatening diseases, such as heart abnormalities, may be necessary for certain kids initially.
Until the anomaly can be corrected, babies with esophageal atresia will require medical assistance to eat. Their doctors will arrange for surgery to fix it as soon as possible. They will be fed in the meantime either intravenously (parenteral feeding) or through a tube (enteral nourishment). Surgery involves:
When your newborn is born with a birth defect that necessitates immediate medical attention, it can be frightening, but for the majority of babies, the emergency is brief in duration. Your medical team will keep an eye on your child until surgery can correct the deformity and restore normal breathing and swallowing. Following surgery, your child may experience some ongoing issues with breathing, swallowing, and respiratory infections, particularly during the first few years of life. However, with continued care and attention, most children grow up to lead relatively normal lives.
Avail expert care for esophageal atresia at Surya Hospital, the best pediatric surgery hospital in Mumbai. Book your consultation now!
Q1. How is esophageal atresia diagnosed?
A: It is often diagnosed shortly after birth through symptoms like excessive drooling, choking, or difficulty feeding. Prenatal ultrasounds may also detect signs.
Q2. Is esophageal atresia life-threatening?
A: Without treatment, it can be life-threatening, but with prompt surgical intervention, most children recover and live healthy lives.
Q3. What causes esophageal atresia?
A: The exact cause is unknown, but it's believed to result from disruptions in fetal development. It may also be associated with other congenital anomalies.
